Choose dried beans or beans canned with low or no sodium. Select dried beans that are dry, firm, clean, uniform in color and not shriveled.
Black-eyed peas, though commonly known as peas, are legumes originating in subtropical Asia. They are famously included in New Year’s Day meals across the southern United States, signifying prosperity. Widely cultivated globally, black-eyed peas are recognized for their distinctive appearance—a dried white bean with a singular black spot. These peas can be harvested as fresh snap beans approximately 60 days after germination or as dry beans around 90 days post-planting. It is best to sow them directly in the garden after the last frost, as they are less successful with transplanting. For an earlier start, consider using black plastic to pre-warm the soil before direct seeding.
Store dried beans at room temperature in a closed container to protect them from moisture and pests.
Black-eyed peas are available in both bush and pole varieties. For fresh snap beans, you can start harvesting 60 to 70 days after planting. If you aim for dried beans, wait about 80 to 100 days. Harvesting dried beans is straightforward: begin picking once the peas are dry on the vine. Bush varieties tend to produce earlier and all at once compared to pole varieties. To extend the bush beans’ production period, stagger your planting every two weeks. For snap beans, pick the pods when they are 3 to 4 inches long, handling them carefully to avoid damaging the vine. For shelling or dry beans, allow the pods to dry fully on the vine until they are brown and the beans inside nearly burst through. After harvesting, shell the pods and let the peas dry completely. Store the dried peas in an airtight container in a cool, dry place for up to a year, and recycle the empty hulls into your compost pile.
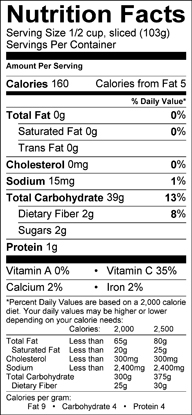
Low in fat and sodium, saturated fat free, cholesterol free, an excellent source of vitamin B1 and a good source of fiber, magnesium, phosphorous and zinc.